Students and Teachers Forum
The industrial areas should be constructed far from human .....
The two effects of air pollution are: 1. Reduction in visibility 2. Depletion of ozone .....
A volcanic eruption and forest .....
The contamination of air with unwanted and harmful substances is called air .....
The contamination of the environment due to mixing of harmful and unwanted substances that makes the environment impure is called environmental .....
The ecological pyramid formed on the basis of the biomass of organisms in each trophic level is called pyramid of .....
The undesirable change in the physical, chemical or biological characteristics of air is called air .....
The finely divided solid or liquid particles suspended in air are called .....
In the flavering plants, during fertilization the male gamete fuses with the diploid secondary nucleus. The secondary nucleus is the fusion product of two polar nuclei and forms the endosperm nucleus. This process is called triple .....
1. It produces new individual having exactly identical qualities as that of parent. 2. It is faster, cheaper and easier method of reproduction. 3. It is useful method of reproduction for the plants which do not produce viable seeds. 4. Off .....
a. Figure (a) shows vegetative propagation. This method is called whip grafting. b. It is amoeba. The method of reproduction shown by b is binary fission and by c is budding. c. It is yeast. d. A is mother yeast. B is a .....
The three applications of tissue culture techniques are: 1. For the production of valuable compounds like plants derived protein used as biopharmaceuticals. 2. To cross distantly related species so as to obtain the hybrid. 3. To conserve rare .....
It is a type of asexual reproduction i.e. Vegetative propagation. The three reasons for applying this method in sugarcane are: 1. It is an easier, cheaper and rapid method of reproduction or propagation of plants. 2. Sugarcane does not .....
The process of deposition of acid gases such as SO2, nitrogen oxide from the atmosphere on land in the form of rain, is called acid .....
In the higher angiosperms two pairs of nuclei fuse in them out of the two pollen grains, one of them fuses with egg nucleus to form embryo while the other (pollen grains) fuses with the secondary nucleus to form endosperm. So, double fertilization .....
Internal fertilization
.....
The hybrids (organisms) provided as a result of cross-pollination are more healthy, vigorous and generally better adapted in the environment in which they live. Therefore, cross-pollination is considered to be superior to .....
Vegetative propagation is beneficial to farmers because of the following reasons. 1. A large number of plants can be propagated easily and cheaply within a short period of time. 2. The plants like a rose, sugarcane, potato, etc. which .....
Self pollination Cross pollination 1. It is the process of transfer of pollen grain from .....
Sexual reproduction involves the fusion of chromosomes in the nuclei of gametes more precisely; it involves the transmission of favourable variation from generation to generation which causes evolution. Due to this many types/variation of plants and .....
A zygote is formed by the fusion of male and female gametes. Each male and female gamete contains haploid in the chromosome. When such haploid gametes fuse together, a diploid cell or structure i.e. Zygote is formed. Male gamete (n) + Female .....
Male gamete Female gamete 1. It is motile and smaller in .....
The process of fusion of nuclei of male and female gamete to form a zygote is called .....
Sugarcane and Rose reproduce by vegetative .....
Gamete Zygote 1. It is haploid.
.....
Zygote is a diploid cell formed after the fusion of male and female .....
a. Chromosomes: Chromosomes are thin hair like structure which is responsible for the inheritance of hereditary characters from parents to the offspring. Each human body cell consists of (diploid) 46 numbers of chromosomes whereas the germ cells i.e .....
In Down's syndrome or Mongolism, there is one additional copy of a 21st chromosome. Down's syndrome is a genetic disorder, it can be identified by the following methods; 1. Blood test to examine the chromosomes. 2. Amniocentesis: In this .....
The functions of chromosomes are; 1. Chromosomes are keys for a cell division. 2. Chromosomes are responsible for the inheritance of hereditary characteristics from parents to their offspring. 3. Chromosomes help in growth and metabolism by .....
Haemophilia is also known as bleeder's diseases. Haemophilia is a sex-linked chromosomal disorder caused due to the defective gene on X-chromosome which cannot produce or synthesize clothing factor i. e factor. People with haemophilia tend to .....
Down's syndrome is called 21 trisomy. It is because the cells of such person contain an additional 21st copy of chromosome number 21 instead of a normal two 21st .....
Mitosis Meiosis
1. It results in two diploid cells. .....
It is the abnormal condition in which there are more or fewer numbers of chromosomes than the normal set (i.e.23pairs in human) of chromosomes. Aneuploids are the organisms resulted from aneuploidy. Aneuploids arise due to a failure of separation of .....
Haemophilia is a genetic disorder associated with 'X' chromosome, the defective genes can be passed from mother to son. Males typically lack a second 'X' chromosomes so they are unable to make up for the defective gene. But, the .....
Klinfelters Syndrome
Down's .....
Disorder or abnormalities which are caused by changes in the gene lying in sex chromosomes are called sex-linked disorders. Examples of such disorders are haemophilia and colour .....
Diploid cells
Haploid .....
Autosomes Sex chromosomes
1. These are responsible for the growth and development of the body along with .....
It is essential for growth and development of the .....
The function of the gene is to give traits like eye colour, hair colour, height etc to the organism by synthesizing .....
A protein known as histones makes chromosomes to be fitted inside the nucleus of the .....
The full form of DNA is Deoxyribonucleic acid and RNA is ribonucleic .....
A pair of chromosomes which is similar in shape, size and function containing a maternal and paternal chromatids joined together at the centromere is called homologous .....
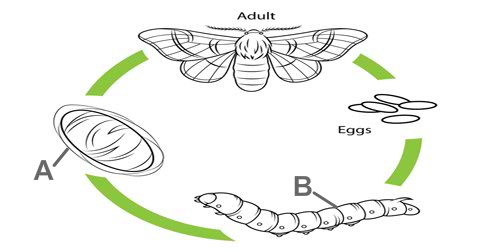
a. Label A and B A is a cocoon, the pupal case secreted by fifth instars larva, B is chrysalis or pupa. b. Which part of them consists of silk? The part A consists of .....
The study of bees concluding honey bees is called .....
It is a biological process by which an organism physically develops after birth or hatching, bringing the rapid change in body .....
The two places in Nepal where sericulture is done are: 1. Bandipur ( Tanahun) 2. Khopasi ( .....
They are worker bees, drones and queen .....
Worker bees are the sterile female bees whose work is to feed larva, protect the beehives, collect nectar .....
On favourable condition, the egg hatches into small caterpillars within 10 to 12 days. The larva is creamy white in colour and is very active that means it is a voracious feeder and moves actively on the leaf. The body of larva contains a head with .....

.png)