Students and Teachers Forum
Let us now substitute the respective values.
.....
The catalyst which decreases the rate of a reaction is called a negative .....
Here, we have to find the voltage in the circuits, power of bulbs and resistance .....
Here, we have to calculate the amount of electrical energy consumed in the primary winding and .....
Here, we have to find the tariff that should be paid.
.....
Here, we have to find the unit of electricity consumed.
.....
Here, we have to sketch diagrams of circuits which give resistances 50 Ω and 200 Ω when two resistances of 100 Ω are in the circuit.
.....
Here, we have to calculate the resistance of a .....
Here, we have to calculate the number of bulbs that can be used in the .....
Here, we have to calculate the power of the bulb.
.....
When ammonia gas is dissolved in water, ammonium hydroxide is .....
When a glass rod dipped in conc. HCl is introduced in a jar containing ammonia gas, it produces white dense fumes of ammonium .....
Ammonia gas is prepared in the laboratory by heating a mixture of dry solid ammonium chloride and slaked .....
Ammonia is a compound made up of nitrogen and .....
Carbon dioxide gas is used to extinguish the fire because it is neither combustible nor helps in combustion and being heavier than air it settles down on the burning surface and forms a layer cutting off the supply of oxygen to .....
Carbon dioxide gas is collected in a gas jar by upward displacement of air because carbon dioxide gas is heavier than .....
When carbon dioxide is passed through lime water, lime water turns milky due to the formation of white suspension of insoluble calcium .....
When carbon dioxide gas is dissolved in water, carbonic acid is .....
Carbon dioxide is prepared in the laboratory by the action of dilute hydrochloric acid on calcium .....
The three applications of neutralization reaction are as follows : a. Farmers use lime in the soil to neutralize the acidic nature of the soil. b. We use antacid (magnesium hydroxide) to reduce the acidity of the stomach. c. Formic acid enters into .....
If almost all the molecules of alkalis dissociate into hydroxyl ions in aqueous solution, they are said to be strong .....
pH is the concentration of H+ ions present in the solution which determines whether a solution is acidic, alkaline or .....
Acids which ionize to a larger extent in aqueous solution and produce high concentration of hydrogen ions are known as strong .....
The hydrated hydrogen ion that exists in the solution of acids is called a hydronium .....
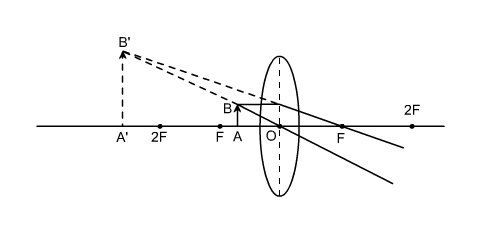
In the figure below, F is the principal focus of the convex lens, O is the optical centre. Thus, the line OF represents focal length (f). The point 2F on the principal axis is at a distance of 2f from the optical centre O. According to the .....
Sewage should be managed .....
In the figure below, F is the principal focus of the convex lens, O is the optical centre. Thus, the line OF represents focal length (f). The point 2F on the principal axis is at a distance of 2f from the optical centre .....
I. The type of defect of vision of eye shown in the diagram is short-sightedness or myopia. It is a defect of vision in which a person cannot see distant objects clearly, but can see nearby objects .....
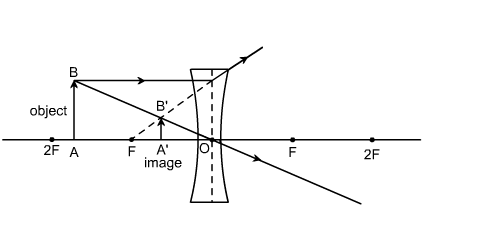
I. In the figure below, F is the principal focus of the concave lens, O is the optical centre. Thus, the line OF represents focal length (f). The point 2F on the principal axis is at a distance of 2f from the optical centre .....
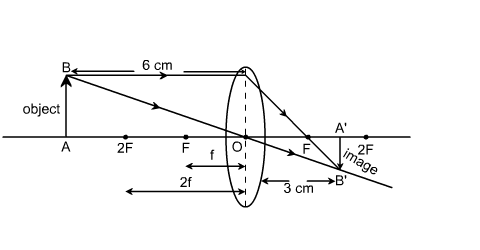
I. In the figure below, F is the principal focus of convex lens, O is the optical centre. Thus, the line OF represents focal length (f). The point 2F on the principal axis is at a distance of 2f from the optical centre O. If f = 3 .....
I. In the figure below, F is the principal focus of the concave lens, O is the optical centre. Thus, the line OF represents focal length (f). The point 2F on the principal axis is at a distance of 2f from the optical centre O. If f = 2 cm, the .....
In the figure below, F is the principal focus of a convex lens, O is the optical centre. Thus, the line OF represents focal length (f). The point 2F on the principal axis is at a distance of 2f from the optical centre O. If f = 3 cm, the point 2F is .....
Here, M is the magnification of lens, .....
Here, P is the power of a lens And f is the focal length of the lens So, to .....
Here, f is the focal length of a lens, .....
Here, .....
The information given are;
.....
The lens which is thick at the middle and thin at the ends is called convex .....
Lens is a portion of a transparent refracting medium, usually glass, bound either by two curved surfaces or by one plane and one curved .....
1. He has short sighted eyes. 2. The inability of ciliary muscles to contract properly is its cause. 3. He is using spectacles with concave lens to remove his defect of vision. 4. The diagram to show the remedy of .....
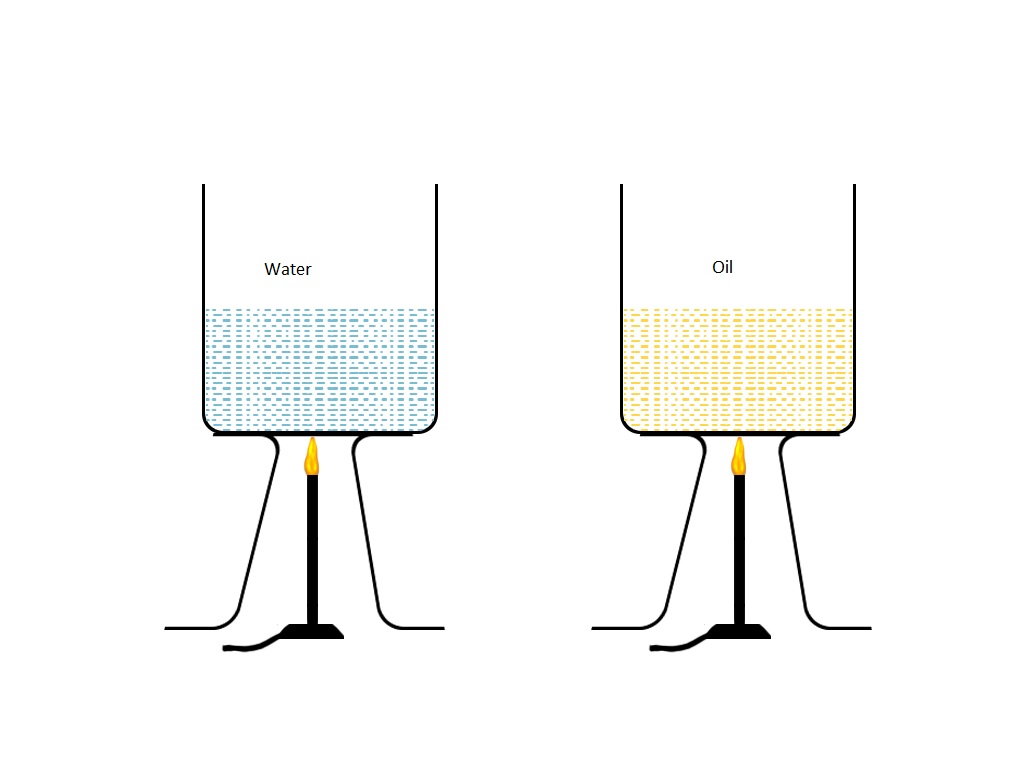
I. If an equal amount of heat is applied to both objects, mustard oil will have more temperature. Because it has lower specific heat capacity in comparison to water and the substance which has less specific heat capacity, change their temperature .....
The differences between clinical and laboratory thermometers are as followings: Clinical thermometer Laboratory thermometer 1. Clinical thermometer is scaled from 35°C to 42°C or from 94°F to 108°F. 1. .....
We have the heat equation, Q = msdt where, m = Mass of body Q = Heat energy of a body s = Specific heat capacity of body dt = change in temperature Hence, quantity of heat energy of an object depends in following .....
I. Here, Given, For iron nail, Mass (m1) = 2 kg Temperature (t1) = 50°C Specific heat capacity (s1) = 470 J/kg°C Heat energy (Q1) =? For water, Mass (m2) = 200 gm. = .2 kg Temperature (t2) = 80°C Specific heat capacity (s) = .....
The distance between the optical center and the principal focus of a lens is known as the focal .....
The point on the principal axis where rays of light parallel to the principle axis after refraction through the lens, converge to a point on the axis or appears to diverge from a point on the axis is called principal .....
Here, Given, For hot water, Mass (m1) = 10 kg Temperature (t1) = 70°C For cold water, Mass (m2) = 20 kg Temperature (t2) = 10°C Specific heat capacity (s) = 4200 J/kg°C Final temperature of mixture (t) =? According to the heat .....
Here, Given, For hot water, Mass (m1) = 10 kg Initial temperature (t1) = 90°C For cold water, Mass (m2) = 20 kg Initial temperature (t2) = 20°C Specific heat capacity (s) = 4200 J/kg°C Final temperature of mixture (t) =? According to .....
Here, Given, For hot water, Mass (m1) = 200 gm. = 0.2 kg Initial temperature (t1) = 40°C For cold water, Mass (m2) = 2 kg Initial temperature (t2) = 30°C Specific heat capacity (s) = 4200 J/kg°C Final temperature of mixture (t) .....
.png)
.png)
.png)